
Defibrillation: Shocking the heart back to a normal rhythm.Radiofrequency ablation: Radiofrequency ablation is a non-invasive procedure that involves ablating (burning) tiny parts of the heart that are causing the irregular beats.Cardioversion a procedure that will shock your heart into rhythm to stop the atrial flutter.Blood-thinning medications that can prevent stroke.Anti-arrhythmia medication: Used to correct the rhythm of the heart.The overall goal of atrial flutter treatment is to bring the heart rhythm back to normal and prevent any clotting from forming. Electrophysiology (EP) studies: An EP study is a more invasive procedure that is used to record the heart's rhythm.Īfter your doctor evaluates your symptoms, they can better determine which treatment would be most appropriate.Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to see your heart's activity visually.Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Used to monitor and track the electrical impulses to the heart.
TREATMENT FOR HEART FLUTTER FULL
Your doctor will look at your medical history and symptoms and will perform a full medical examination and perform any of the following diagnostic tests:
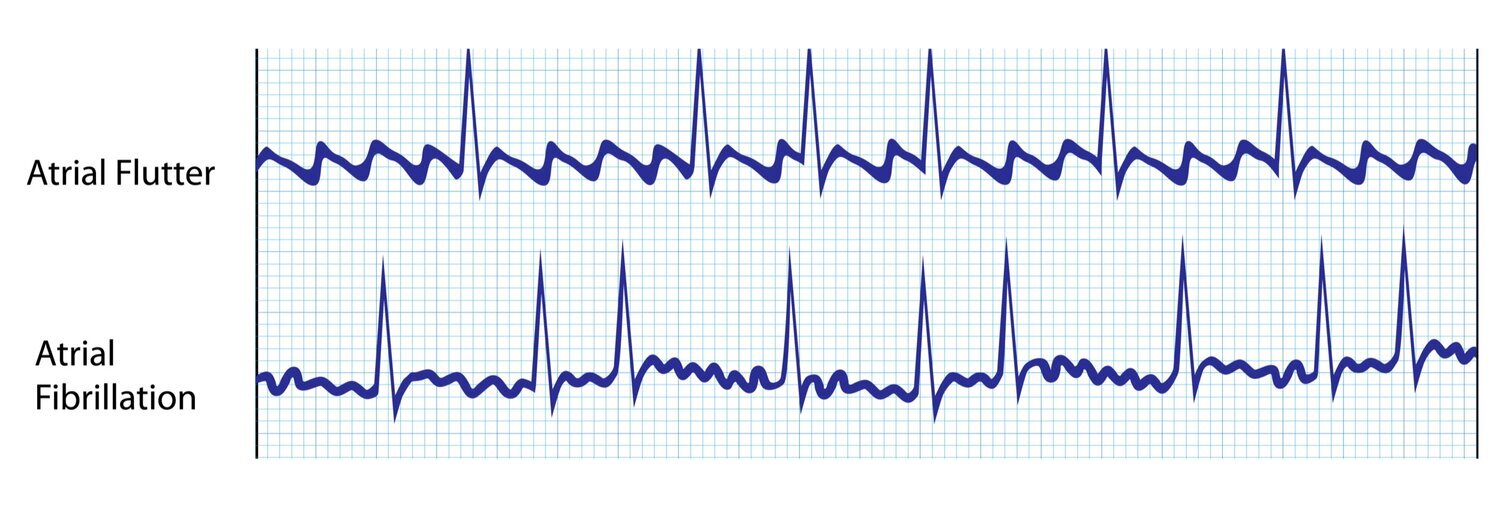
Atrial flutter causesĪFL can be caused by several conditions and factors, including: If left untreated, the rapid heart rate can lead to heart failure, heart attack, or stroke. However, the most common symptom is rapid heartbeat.

In some cases, it is possible symptoms might not be felt. People with AFL tend to have a steady heart rate, even though it is faster. While atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation are similar, atrial flutter is less chaotic and more organized. As a result, blood is not pumped effectively through the heart and to the body. AFL occurs when the atria beat at an excessive rate of 250-400 beats per minute. Atrial flutter occurs in the upper chambers of the heart (atria).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
